- Cores and Threads: The processor has 16 cores, which are divided into 6 performance cores, 8 efficient cores, and 2 low-power efficient cores, leading to a total of 22 threads.
- Clock Speed: The base clock frequency is 3800 MHz, with a maximum turbo frequency of 4.8 GHz.
- Cache: It features a 24MB L3 cache.
- Thermal Design Power (TDP): The TDP ranges from 20 to 65 watts, with a maximum boost up to 115 watts.
- Transistor Size: The processor is built on a 7 nm technology.
- Architecture and Socket: It uses the Meteor Lake architecture and is designed for a custom socket, specifically BGA 2049.
- Cores and Threads: This processor has 8 cores and 16 threads, enabled by AMD Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT).
- Clock Speed: The base clock is set at 3300 MHz, with a maximum turbo frequency of up to 5100 MHz.
- Cache: It has a 16MB L3 cache.
- Thermal Design Power (TDP): The TDP is specified at 15-30 watts.
- Transistor Size: It’s built on a 4 nm technology.
- Architecture and Socket: The Ryzen 7 7840U is part of the Ryzen 7 lineup, using the Zen 4 (Phoenix) architecture, and is compatible with the socket FP8.
In summary, the Intel Core Ultra 7 155H has more cores and threads, a larger cache, and a higher TDP, which might indicate higher power consumption but potentially more raw processing power. On the other hand, the AMD Ryzen 7 7840U, with fewer cores and a smaller cache, operates at a higher clock speed and is built on a more advanced 4 nm technology, suggesting better efficiency. The choice between these processors would largely depend on specific use cases and preferences for power efficiency versus processing capabilities.
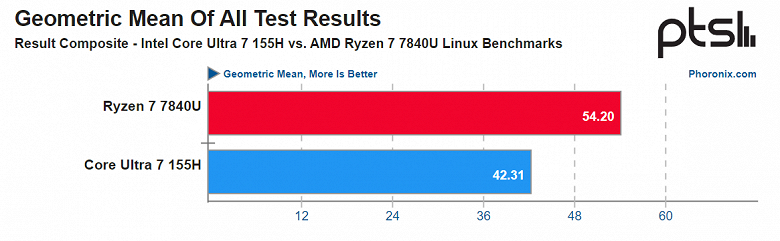
In a comprehensive performance comparison conducted under the Linux environment, the AMD Ryzen 7 7840U significantly outperformed the Intel Core Ultra 7 155H. This extensive study included 370 benchmark tests covering a wide range of applications, including browser performance, high-performance computing (HPC), content creation, video encoding, code compilation, audio encoding, AI tests, and scripting in various languages.
Key findings from the comparison are as follows:
- Overall Performance: The AMD Ryzen 7 7840U led the Intel Core Ultra 7 155H in nearly 80% of the 370 tests conducted. This dominance was particularly noticeable in terms of energy efficiency and overall performance. On average, the Ryzen 7 7840U was 28% faster than the Intel processor while consuming similar or even less power.
- Testing Environment: The tests were conducted on laptops with both processors, running Ubuntu 23.10 with the Linux kernel 6.7-rc5. Both devices were equipped with 16 GB of RAM. The Ryzen 7 7840U model (Framework 13) featured 8 cores, 16 threads, and a 16 MB L3 cache, with a clock speed of up to 5.1 GHz and a TDP ranging from 28 to 30 watts. In contrast, the Intel Core Ultra 7 155H (in an ACER Swift laptop) had 16 cores, 22 threads, and a 24 MB L3 cache, with a TDP varying from 28 to 115 watts.
- Future Testing Plans: Additional tests are planned, including comparisons of integrated GPUs and AI performance on NPUs (Neural Processing Units). Despite AMD’s current lead, it is expected that Intel will continue optimizing the performance of its chips, especially in light of AMD’s upcoming Ryzen 8000 series featuring faster NPUs.
This comprehensive analysis underlines the AMD Ryzen 7 7840U’s superior performance and energy efficiency in a Linux environment, a significant consideration given the expectations from Intel’s new Meteor Lake architecture.
Pricing Revealed for AMD Ryzen 7 5700X3D, Ryzen 5 5600GT, and 5500GT Processors